Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disease, characterized by progressive cognitive impairment, disorientation, executive dysfunction, and personality and behavior changes. According to the recent Alzheimer’s Disease International, approximately 55 million people globally are suffering from dementia, with the number expected to reach 139 million by 2050. Alzheimer’s disease accounts for more than half of these cases.
Hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease
The two pathological hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease are amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). Amyloid plaques arise from improper cleavage of the amyloid precursor protein (APP), resulting in aggregates of amyloid-beta (Aβ) monomers that form plaques. Neurofibrillary tangles are caused by the aggregation of hyperphosphorylated tau protein (pTau), which disrupts microtubule stabilization and intracellular trafficking, leading to neuronal death.
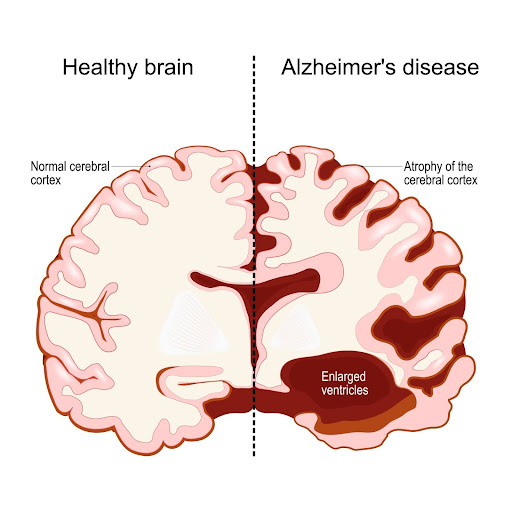
Figure 1: Comparison of the stark differences between a healthy brain and one affected by Alzheimer’s disease. This image illustrates the profound impact of Alzheimer’s, highlighting the significant loss of brain volume and structure in AD patients compared to normal individuals. (Shutter Stock)
https://www.shutterstock.com/vi/image-vector/human-brain-two-halves-healthy-alzheimers-2381072271
Despite decades of research into these pathologies, while there are medications prescribed for Alzheimer’s patients, none currently offer a solution for regenerating brain cells themselves. This has highlighted the urgent need to improve our understanding of AD pathogenesis and explore new therapeutic approaches.
Stem cell therapy may offer potential for Alzheimer’s disease treatment due to its ability to target multiple pathogenic mechanisms. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are currently the most widely used stem cell type in Alzheimer’s disease clinical trials. According to researchers from Huazhong University of Science and Technology, MSCs offer several mechanisms of action that make them suitable for Alzheimer’s disease therapy.
In Alzheimer’s, the loss of neurons and the deterioration of synaptic connections are primary contributors to cognitive decline. MSCs can potentially replace damaged or lost neurons by differentiating into neural cells. This cell replacement effect is crucial in restoring neural function and improving cognitive abilities.
Neuroinflammation plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Chronic activation of the brain’s immune cells leads to the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which contribute to neuronal damage. This persistent inflammation exacerbates amyloid-beta accumulation and tau pathology, driving further neurodegeneration and cognitive decline. In stem cell treatment, Mesenchymal stem cells can convert microglia and astrocytes from
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/cellular-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fncel.2021.811852/full
pro-inflammatory phenotypes to anti-inflammatory phenotypes, thereby reducing the neuroinflammatory response and neuronal damage. Studies have demonstrated that MSC transplantation can improve cognitive function and reduce amyloid deposition and pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in Alzheimer’s disease models.
MSCs not only promote angiogenesis but also stimulate endogenous neurogenesis, aiding in the repair and regeneration of neuronal tissues. They might have potential to enhance the clearance of amyloid-beta (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs), which are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. This reduction in pathological protein aggregates helps to mitigate the progression of the disease. Furthermore, MSCs improve autophagy, a critical cellular process that removes damaged organelles and proteins, thereby maintaining cellular homeostasis. They also contribute to the renormalization of the blood-brain barrier, which is often compromised in Alzheimer’s patients, restoring its integrity and function.
Leading the Way at Korokai Medical Corporation
At Korokai Medical Corporation, our regenerative medicine department is at the forefront of developing innovative treatments for Alzheimer’s disease using mesenchymal stem cell therapy. Our cutting-edge research and clinical trials focus on harnessing the regenerative capabilities of MSCs and their secretome to target the multiple pathogenic mechanisms of AD.
Our work aims to bridge the gap between basic science and clinical intervention, offering new hope for patients suffering from Alzheimer’s disease. By leveraging the therapeutic potential of MSCs, we are dedicated to improving the quality of life for AD patients and advancing the field of regenerative medicine.
As we continue to explore the full potential of stem cell therapy in Alzheimer’s disease, Korokai Medical Corporation remains committed to pioneering innovative treatments and providing hope for millions affected by this devastating condition.